Equine Standing CT: Diagnosing the 6 Most Common Head and Neck Injuries
In the world of equine medicine, advancements in imaging technology have revolutionized the way veterinarians diagnose and treat injuries in horses. One of the most valuable tools in this regard is the equine standing computed tomography (CT) scanner. Done under sedation, this non-invasive imaging technique allows for high-resolution, three-dimensional visualization of the head and neck, making it a vital tool for identifying a wide range of injuries that can impact a horse's well-being and performance. Here, we explore the 6 most common head and neck injuries diagnosed with Equina® standing CT scanner.
Fractures
23yo QH mare with head trauma and fracture of zygomatic bone
Equine athletes are susceptible to a variety of fractures, and those affecting the head and neck can be particularly challenging to diagnose without the aid of advanced imaging. Fractures in the skull, mandible, and cervical vertebrae can occur due to traumatic accidents or repetitive stress, a prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for successful management. The Equina standing CT allows veterinarians to assess the exact location and severity of fractures, providing critical information for treatment decisions.
Case Study: 23yo QH presented with trauma to head which occurred three days prior with developing draining tract. Findings: Open, complete, comminuted, articular fractures of the left zygomatic temporal bone and coronoid process of the mandible. Displacement of fracture fragments, soft tissue swelling (cellulitis, hemorrhage and/or edema) and subcutaneous emphysema +/- osteomyelitis and sequestrum formation. Multifocal periodontal and endodontic disease, rostral and caudal hooks, and wave mouth.
Cervical Vertebrae Injuries
14yo Appaloosa with subluxation and spinal cord compression
The cervical spine is crucial for stability and movement of the horse's head. Injuries to these vertebrae can result in pain, neurological deficits, and even paralysis. Equina standing CT allows for precise visualization of these delicate structures, aiding in the detection of fractures, dislocations, and spinal cord compression. Treatment options include rest, immobilization, and in some cases, surgical intervention to ensure proper healing and prevent long-term complications.
Case Study: 14yo Appaloosa presented with toe dragging and dilated pupils and swelling over the C2/C3 region. Radiographs taken with no diagnosis made. Unable to stand, the patient was scanned under GA on mobile transport table, in dorsal recumbency. Findings: C2/C3 subluxation with osseous fragments and compression to the spinal cord. (The horse was humanely euthanized.)
Sinus Infections and Disorders
7yo Quarter Horse with sinusitis and tooth root abscess
Horses can develop sinusitis, sinus cysts, or other sinus-related disorders, which can lead to a range of issues if left untreated. With Equina standing CT, veterinarians can evaluate the paranasal sinuses, identifying any signs of inflammation, fluid accumulation, or structural abnormalities. This allows precise treatment plans for the patient that may involve drainage, medication, or surgical intervention.
Case Study: Dorsal (A) and transverse (B) multiplanar reconstructed CT images of a 7-year-old Quarter Horse with diffuse right rostral and caudal maxillary paranasal sinusitis (red arrows). Fluid secondary to lysis of the periapical alveolar bone of the maxillary molar tooth (tooth 111), likely due to tooth root infection (yellow arrow), can be seen. source
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
18yo Tennessee Walking Horse with OA and TMJ
TMJ disorders can cause significant discomfort for horses and impact their ability to chew, swallow, and perform at their best. The Equina standing CT provides detailed images of the temporomandibular joint, allowing veterinarians to assess any abnormalities in this critical joint. Diagnosing TMJ issues early is essential for managing pain and preventing further deterioration.
Case Study: 18yo Tennessee Walking Horse with historic temporomandibular enlargement. Findings: Severe bilateral temporomandibular joint disease with mineralized menisci and/or bone fragments, with associated mass effect on the guttural pouches and right basisphenoid bone. Differential diganosis: Degenerative joint disease or non-union of chronic fractures.
Soft Tissue Pathology
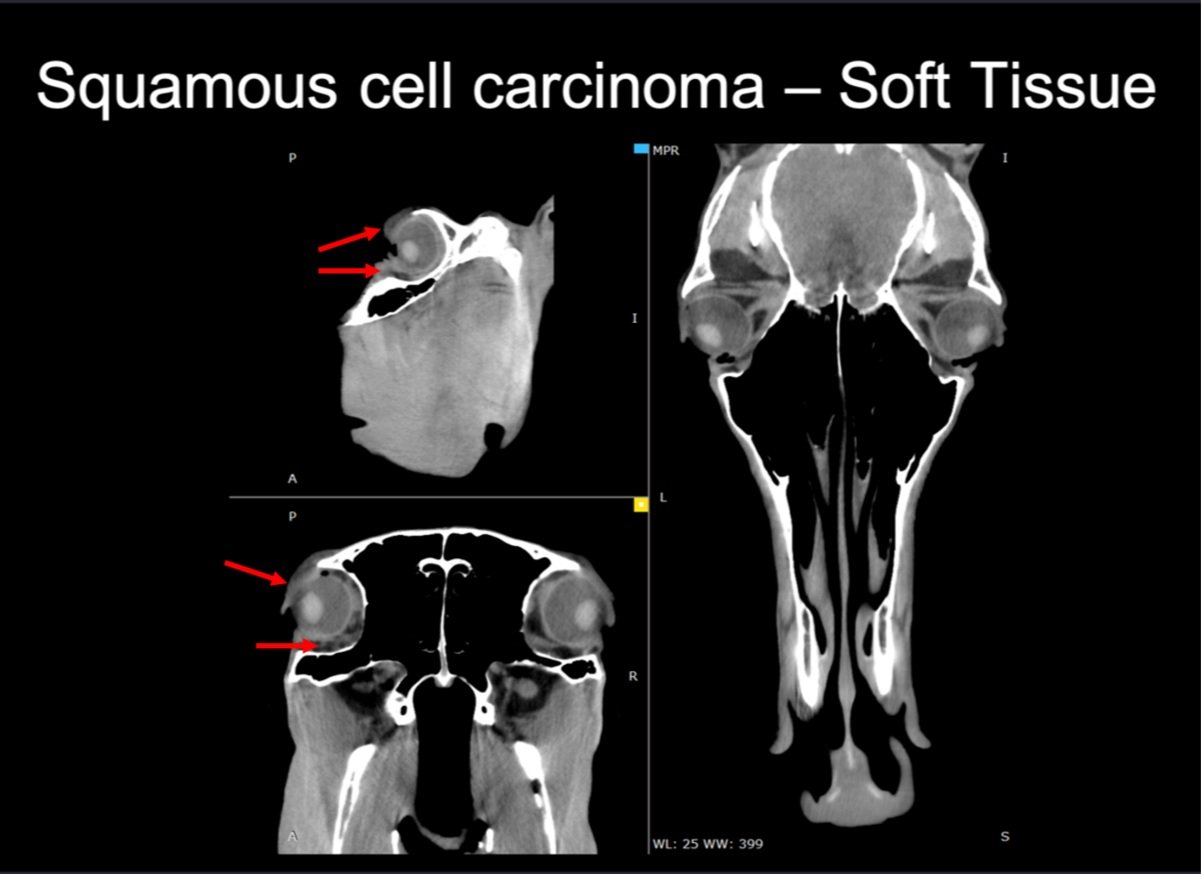
23yo Standardbred with SCC
While many imaging techniques focus on bone injuries, equine standing CT with fan-beam technology is exceptional for detecting soft tissue pathology in the head and neck region. Lymph nodes, guttural pouches, sinus cysts and other soft tissue problems can be visualized with this technology, aiding veterinarians in understanding the extent of the pathology and developing appropriate treatment plans.
Case Study: 23yo Standardbred with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), images shown with the soft tissue filter. Red arrows point to the SCC in and around the orbit.
Osteoarthritis
2yo Morgan with Neurologic Disorder
As horses age or experience repetitive stress, they can develop osteoarthritis in the head and neck, leading to pain and reduced mobility. The Equina standing CT provides a comprehensive view of the joints in this region, helping veterinarians assess the degree of arthritis and guiding decisions for pain management, rehabilitation, and maintaining the horse's quality of life.
Case Study: 2yo Morgan with neurologic disorder, images shown with the bone filter. Caudal C2 end-plate destruction and proliferation with rostral C3 sclerosis and narrow disk space. Arrows point to where the pathology is changing.
Equine standing CT has revolutionized the diagnosis and management of head and neck injuries in horses, offering detailed insights into complex anatomical structures. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the use of standing CT will become even more integral in the field of equine veterinary medicine, allowing for earlier and more effective intervention in cases of head and neck injuries.
All of the cases above were captured with the Equina® CT scanner. To learn more about the Equina and its cutting-edge technology that provides a swift and stress-free scanning process. Please click the button below.